MongoDB is a leading NoSQL (Not Only SQL) database management system, renowned for its flexibility and scalability. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents instead of rigid tables with fixed schemas. This document-oriented architecture enables seamless handling of diverse data types and structures.

Key Features of MongoDB
- Document-Oriented Storage: MongoDB stores data in documents, typically in BSON (Binary JSON) format, allowing for nested data structures and dynamic schemas.
- Flexible Schema: MongoDB does not enforce a predefined schema, enabling developers to evolve data structures organically as application requirements change.
- Scalability: MongoDB scales horizontally across multiple servers, facilitating distributed data storage and high throughput.
- High Performance: With features like in-memory computing, automatic sharding, and replica sets, MongoDB delivers exceptional performance and fault tolerance.
- Rich Query Language: MongoDB offers a powerful query language supporting various operations such as filtering, sorting, and aggregation.
- Indexing: MongoDB supports different types of indexes to optimize query performance, including single-field, compound, geospatial, and text indexes.
- Ad Hoc Queries: Developers can perform ad hoc queries without predefined schemas, facilitating rapid prototyping and iterative development.
- Aggregation Framework: MongoDB’s aggregation framework enables complex data aggregation operations like grouping, filtering, and transformation.
- Replication and High Availability: MongoDB supports replica sets for automatic failover and data redundancy, ensuring high availability and data durability.
- Community and Enterprise Editions: MongoDB offers both open-source community and commercial enterprise editions, catering to diverse needs with additional features and support in the enterprise version.
Use Cases of MongoDB
- Web Applications: MongoDB is well-suited for web applications requiring flexible data models and horizontal scalability, such as e-commerce platforms and content management systems.
- Mobile Apps: Its support for offline data storage and synchronization makes MongoDB an ideal choice for mobile app development.
- IoT (Internet of Things): MongoDB’s ability to handle diverse data types and high throughput makes it suitable for IoT platforms managing sensor data and device telemetry.
- Real-Time Analytics: MongoDB’s aggregation framework enables real-time analytics on large datasets, powering data-driven decision-making in various industries.
- Content Management: Content-heavy applications benefit from MongoDB’s document-oriented storage, enabling efficient management of multimedia content and metadata.
How to Access Data in MongoDB?
There are a variety of methods for accessing and interacting with data. Whether you prefer a graphical user interface, command-line interface, cloud-based management, or programmatic access, MongoDB provides versatile tools to suit your preferences and use cases.
The four common approaches to access data in MongoDB: MongoDB Compass, MongoDB Shell, MongoDB Atlas, and MongoDB Drivers.
MongoDB Compass
MongoDB Compass is a powerful graphical user interface (GUI) tool which provides a user-friendly environment for interacting with MongoDB databases, making it ideal for users who prefer a visual approach.
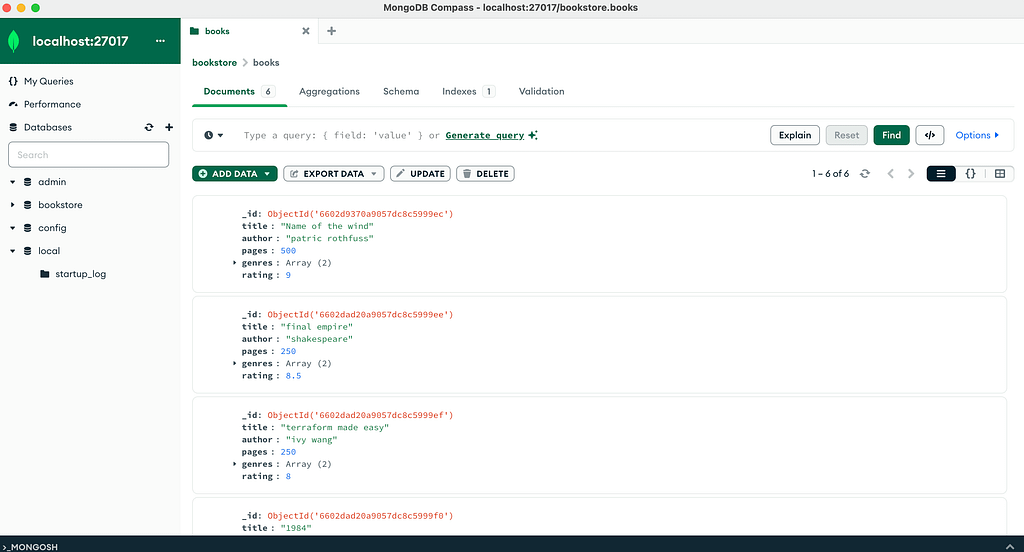
MongoDB Shell
For users who prefer command-line interaction, MongoDB Shell provides a JavaScript-based shell for accessing MongoDB databases. MongoDB Shell offers:
- Connectivity to MongoDB instances locally or remotely.
- Execution of queries, updates, and administrative commands using JavaScript syntax.
- Full access to MongoDB Query Language (MQL) for complex operations.
- Administration tasks such as database and collection creation, user management, and more.

MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service which simplifies the deployment, management, and scaling of MongoDB databases in the cloud. With MongoDB Atlas, users can:
- Create and configure MongoDB clusters quickly and easily.
- Monitor database performance and health in real-time with comprehensive dashboards.
- Automatically scale resources to meet changing workload demands.
- Integrate with other cloud services and platforms for seamless application development and deployment.

MongoDB Divers
MongoDB offers official and community-supported drivers for various programming languages and platforms such as Java, JavaScript, PHP and Python.
Example of MongoDB Python Driver
from pymongo import MongoClient
# Connection URI
uri = "mongodb://localhost:27017"
# Connect to MongoDB server
client = MongoClient(uri)
print("Connected to MongoDB")
# Access database and perform operations
db = client['mydatabase']
# Example: Insert document into collection
result = db['mycollection'].insert_one({'name': 'John', 'age': 30})
print("Document inserted:", result.inserted_id)
# Close connection
client.close()