In the preceding section, we explored the basics syntax of HCL. Now, let’s highlight one for Terraform’s coolest features: its declarative philosophy.
This approach allows you to define and set up infrastructure resources using a simple configuration language. Terraform only looks at where you are (initial state) and where yo want to be (destination state), applying only the right and necessary changes to get there. Which means, you don’t have to worry about what’s happening in between or write loads of extra code.
The core Terraform workflow consists of only four steps:
- init — Initialize your workspace so Terraform can apply your code.
- write — Express your infrastructure needs using code. Just like telling Terraform what you want in a language it understands.
- plan — Get a sneak peek at all the changes Terraform is about to make, so you’re always in the know and avoid the human-error.
- apply — Execute the changes from your plan, and watch Terraform create, update, or destroy resources as needed.
init
The first command to run for a new configuration—or after checking out an existing configuration from version control—is terraform init. This will initialize various local settings and data that will be used by subsequent commands.
terraform init
Although the concise description is only just two words, this command undertakes various essential tasks behind the scenes. For instance, it initializes the associated backend, whether local or remote. In cases where the configuration involves provider plugins, the command seamlessly downloads and installs the required provider plugins. Furthermore, terraform init sets up modules if they exist in your code. Additionally, the command takes care of the automatic setup of the local Terraform state, streamlining the overall configuration process.

Initialize Terraform in empty directory
This is the output when I just execute this command. As you can see, it create an empty directory and reports you the state of the directory.
plan
terraform plan command is crucial for understanding the changes that will be applied to your infrastructure before actually making those changes. After executing the command terraform plan, it will examine your current state and compares it to the desired state defined in your Terraform configurations (e.g., main.tf)
terraform plan
It’s important to note that the plan command itself doesn’t execute the proposed changes. Instead, you can leverage this command to verify whether the expected modifications align with your intentions before applying them or sharing the alterations with your team for quality control review.
For each resource that is part of the plan, Terraform indicates the action it will take. Common actions include:
+for resources that will be added.-for resources that will be destroyed.~for resources that will be modified.
If Terraform determines that no changes are necessary for resource instances or root module output values, the terraform plan will report that no actions need to be taken. This proactive approach ensures a thorough understanding of potential alterations and promotes a secure environment for implementing changes.
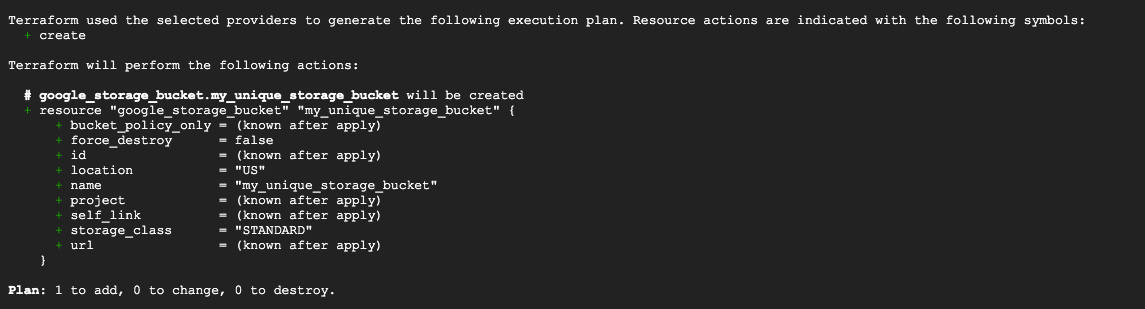
Terraform plan to review the config
In the chart above, I plan to create a storage bucket named ‘my_unique_storage_bucket.’ The ‘+’ symbol indicates that I am in the process of creating a new resource. Notice, in the review plan prcoess, only one resouce is added, there is no change nor destroy.
apply
terraform apply is used to apply the changes specified in plan. Upon executing the command, it carefully reviews the proposed changes and prompt you to confirm that you want to apply the changes. You need to type yes to proceed. Then Terraform will begin the execution process, applying the changes outlined in the execution plan.
terraform apply
The output will display real-time feedback on each step of the application process. You’ll see information about the resources being created, modified, or destroyed.If there are errors or issues, Terraform will provide relevant information to help you understand what went wrong. Once the apply process is complete, Terraform will provide a summary of the changes applied, any errors encountered, and the time taken to complete the operation.
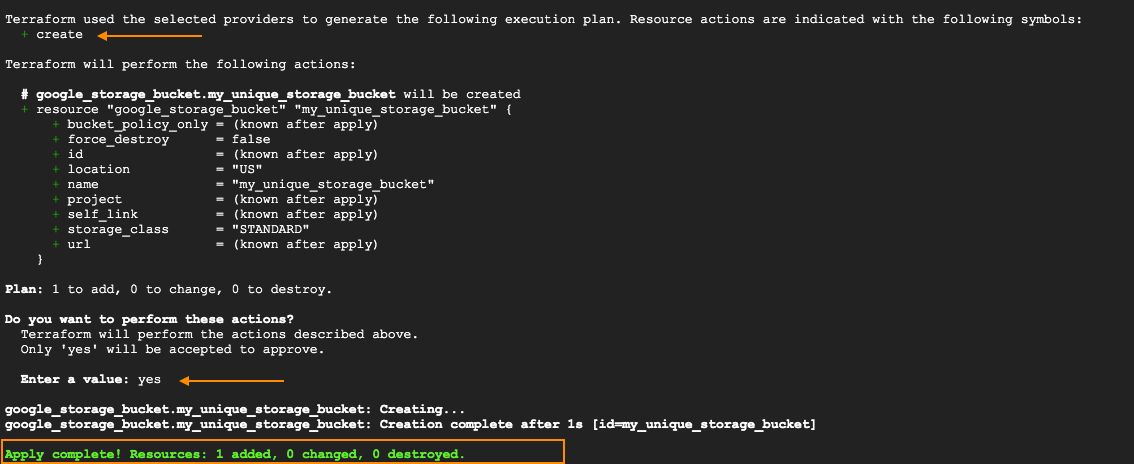
Terraform apply to execute the config
As you can see from the graph above, the process begins with Terraform reviewing the plan, assessing it as a ‘create’ task. Then It displays the entire task and asks your approval. In the ‘Enter a value’ section, you need to manually type ‘yes’ to confirm the modification. Subsequently, the command initiates the execution of the change and provides a comprehensive notification upon completion.
Reformat
To reformat your Terraform configuration in the standard style, use terraform fmt
Validate
To check whether your configuration is valid, use terraform validate
Delete Resource
Remove resources previously applied with your Terraform configuration, use terraform destroy